надо срочно сюда
что-нибудь добавить
Новинки за февраль 2026 года: Квиз для OpenCart, Redirect & Loop Monitor, Админ-панель на сайте, Коллекция брендов.
Это не "ещё один модуль отзывов". Это контентная машина для магазина на OpenCart: отзывы превращаются в SEO-посадочные страницы, медиа-галерею уровня маркетплейсов и инструмент повышения конверсии.
Самые продаваемые в январе 2026 года шаблоны и дополнения: Персональные данные, Стриж, Уведомление о cookie, шаблон Frame.
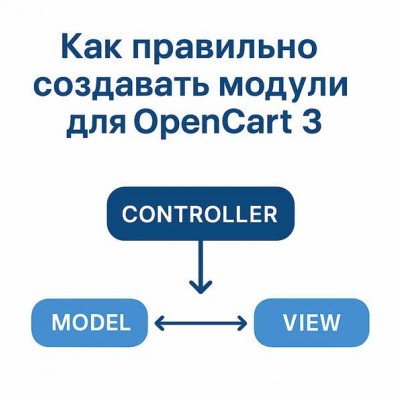
Модуль для OpenCart 3 - это не только рабочий функционал, но и грамотный подход к коду и структуре. Непродуманный код может отпугнуть покупателей, а правильный стиль разработки повышает доверие и облегчает работу с вашим продуктом. Ниже будет несколько советов, возможно они помогут вам в разработке. Если вы хотите что-то добавить или изменить в тексте - пишите в комментариях или на почту.
Этот раздел задает общий подход к оформлению кода и единые ожидания для команды. Простые правила повышают читаемость и снижают стоимость поддержки.
Здесь собраны короткие и проверяемые правила форматирования и именования. Они помогают держать код в одном стиле.
if, foreach, function).=, ==, +, .), после запятых.
class ControllerExtensionModuleLiveExample extends Controller {
public function index() {
$this->load->language('extension/module/live_example');
$data['example_status'] = $this->config->get('module_live_example_status');
if ($data['example_status']) {
return $this->load->view('extension/module/live_example', $data);
}
}
}
Определяем где хранить логику, данные и представление. Четкая структура делает проект предсказуемым и удобным для доработок.
language/.{{ variable }}, {% if %}), не PHP.Обозначаем роли основных слоев. Четкие границы упрощают тестирование и повторное использование кода.
Модель
Задача: работа с базой данных, SQL-запросы и возврат данных.
public function getCustomerByEmail($email) {
$sql = "SELECT * FROM " . DB_PREFIX . "customer WHERE email = '" . $this->db->escape($email) . "'";
$query = $this->db->query($sql);
return $query->row;
}
Контроллер
Задача: работа с $this->request, вызов моделей, формирование $this->response. В контроллере не должно быть SQL и сложной бизнес-логики.
public function getCustomer() {
$this->load->model('account/customer');
$email = $this->request->get['email'];
$customer = $this->model_account_customer->getCustomerByEmail($email);
$this->response->setOutput(json_encode($customer));
}
Библиотека
Задача: хранить бизнес-логику модуля, которая может использоваться из разных мест (фронт, админка, крон).
class Bonus {
public function calculate($order_total) {
return floor($order_total * 0.05);
}
}
Преимущества разделения
Собираем базовые практики защиты и проверки совместимости. Эти шаги снижают риски и продлевают жизнь коду.
$this->db->escape() и (int) для SQL-запросов.htmlspecialchars или html_entity_decode при выводе.mysql_*, ereg, split).mb_*.Здесь показано как безопасно принимать данные и готовить запросы. Примеры можно сразу вставить в рабочий код.
Неправильно (параметры из request прямо в SQL):
$query = $this->db->query("SELECT * FROM " . DB_PREFIX . "customer WHERE email = '" . $this->request->post['email'] . "'");
Если злоумышленник введет ' OR 1=1 --, запрос вернет всех пользователей.
Правильно (контроллер валидирует, модель работает с аргументами):
Контроллер:
public function info() {
// 1) получаем и валидируем email
$email = trim($this->request->post['email'] ?? '');
if (!filter_var($email, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL) || mb_strlen($email) > 96) {
$this->response->addHeader('Content-Type: application/json');
$this->response->setOutput(json_encode(['error' => 'Некорректный email']));
return;
}
// 2) работаем через модель
$this->load->model('account/customer');
$customer = $this->model_account_customer->getCustomerByEmail($email);
$this->response->addHeader('Content-Type: application/json');
$this->response->setOutput(json_encode($customer));
}
Модель:
public function getCustomerByEmail($email) {
$email = $this->db->escape($email);
$query = $this->db->query(
"SELECT * FROM " . DB_PREFIX . "customer WHERE email = '" . $email . "'"
);
return $query->row;
}
Для числовых значений используйте явное приведение и простую валидацию:
Контроллер:
$order_id = (int)($this->request->get['order_id'] ?? 0);
if ($order_id <= 0) {
$this->response->addHeader('Content-Type: application/json');
$this->response->setOutput(json_encode(['error' => 'Некорректный order_id']));
return;
}
$this->load->model('account/order');
$order_info = $this->model_account_order->getOrder($order_id);
$this->response->addHeader('Content-Type: application/json');
$this->response->setOutput(json_encode($order_info));
Модель:
public function getOrder($order_id) {
$query = $this->db->query(
"SELECT * FROM " . DB_PREFIX . "order WHERE order_id = " . (int)$order_id
);
return $query->row;
}
Золотое правило: строки через $this->db->escape(), числа через (int) или (float). Не используйте $this->request внутри модели.
Показываем как оформлять запросы так, чтобы их было удобно читать и расширять. Единый стиль ускоряет ревью и снижает число ошибок.
Для коротких запросов можно использовать одну строку:
$query = $this->db->query("SELECT * FROM " . DB_PREFIX . "customer WHERE customer_id = " . (int)$customer_id);
Но для длинных запросов рекомендуется многострочный формат:
$query = $this->db->query("
SELECT p.product_id, p.model, pd.name, p.price
FROM " . DB_PREFIX . "product p
LEFT JOIN " . DB_PREFIX . "product_description pd ON (p.product_id = pd.product_id)
LEFT JOIN " . DB_PREFIX . "product_to_category p2c ON (p.product_id = p2c.product_id)
WHERE pd.language_id = " . (int)$this->config->get('config_language_id') . "
AND p.status = '1'
AND p.date_available <= NOW()
ORDER BY p.date_added DESC
LIMIT 20
");
Разбираем варианты подключения своих классов. Выбор зависит от того, где нужен объект и когда его лучше инициализировать.
1. Через реестр в catalog/startup/startup.php
Подходит, если библиотека должна быть доступна глобально на фронте сразу после старта.
system/library/MyLib.php или в catalog/library/MyLib.php.catalog/controller/startup/startup.php добавьте регистрацию:
// Если библиотека в system/library:
// $this->load->library('mylib');
// $this->registry->set('mylib', $this->mylib);
// Если библиотека в catalog/library:
require_once(modification(DIR_CATALOG . 'library/mylib.php'));
$this->registry->set('mylib', new MyLib($this->registry));
Плюсы: единая точка инициализации, доступность везде. Минусы: объект создается на каждом запросе, даже если не используется.
2. Локально через require modification(...) в месте использования
Подходит для ленивого подключения только там, где реально нужно.
require_once(modification(DIR_SYSTEM . 'library/mylib.php'));
$mylib = new MyLib($this->registry);
$result = $mylib->doWork($params);
Плюсы: подключение по требованию. Минусы: подключение придется повторять или вынести в helper.
3. Через загрузчик OpenCart: $this->load->library()
Стандартный способ, если библиотека находится в system/library.
$this->load->library('mylib'); // ищет system/library/mylib.php
$this->mylib->doWork($params); // объект доступен как $this->mylib
Рекомендация: если библиотека лежит в system/library - используйте $this->load->library(). Если нужна ранняя глобальная инициализация - регистрация в startup.php. Если библиотека в другом каталоге - подключайте через require modification(...).
Комментарии дополняют код и поясняют намерение. Короткие и точные описания экономят время на чтение.
/**
* Получение списка товаров для примера
*
* @param int $limit Количество товаров
* @return array Список товаров
*/
public function getProducts($limit = 10) {
$query = $this->db->query("SELECT * FROM " . DB_PREFIX . "product LIMIT " . (int)$limit);
return $query->rows;
}
Версия служит ориентиром для обновлений и поддержки. Прозрачность уменьшает количество обращений в техподдержку.
Показывайте номер версии в настройках модуля. Это упрощает поддержку и исключает путаницу.
class ControllerExtensionModuleMyModule extends Controller {
private $module_version = '1.0.0';
public function index() {
// ... ваша логика
$data['module_version'] = $this->module_version;
return $this->load->view('extension/module/my_module', $data);
}
}
<div class="text-muted">Версия модуля: {{ module_version }}</div>
Совет: номер версии должен совпадать с версией в архиве и в CHANGELOG, чтобы клиент всегда видел актуальную информацию.
Хорошо сделанный модуль для OpenCart 3 - это чистый и структурированный код с единым стилем.
Это снижает количество вопросов, увеличивает доверие и помогает продавать модуль эффективнее.
zip -r9 <название_модуля>.ocmod.zip ./upload ПС убил кучу времени на выяснение почему не устанавливается модуль, а "ларчик просто открывался" ))